Did you know that making one ton of virgin cardboard requires three tons of trees? It’s also been estimated that half of the 85 million tons of paper consumed in the US every year is for wrapping and packaging products.
As always, the best way to reduce your impact on the environment is to reduce your use of these items – buy local to avoid the need of shipping in cardboard boxes and purchase in bulk to avoid unnecessary packaging. But if you find yourself with cardboard boxes you need to get rid of, the second-best option is to recycle, as most of these materials are inherently circular in their recycling processes and can be broken down to be remade into new boxes if placed in the correct waste stream. Let’s dive into the life of cardboard.
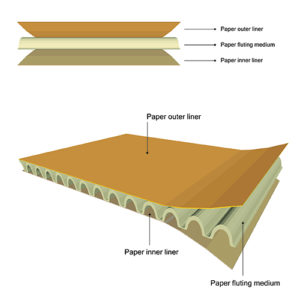
How is cardboard made?
It’s important to understand the production and creation of cardboard. The key raw material in cardboard boxes is paper which comes from trees. A series of linked machines are used to create and form the cardboard boxes in the box plant factories.
First, the paper is fed into the corrugator where it’s formed into the box. One roll of cardboard is corrugated and then glued between two other layers. Corn starch glue is used to bond the wavy corrugated layer to the lining layers. Each layer is comprised of different grades of paper for strength and longevity. The outer layers are typically made from softwood pulp and the lining is typically made from hardwood or recycled fibers.
After the box is put together, the trimmer cuts out the small details, such as the flaps and hand holes, and scores the creases for folding.
How should cardboard be prepared to recycle it?
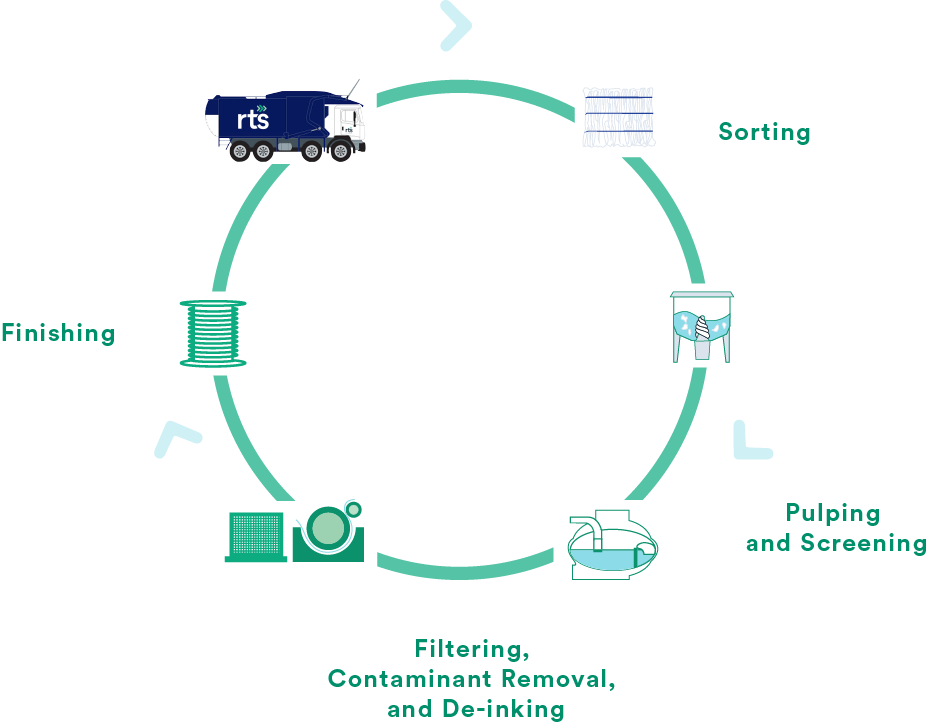
At the end of its life cardboard should be broken down, tape and stickers removed and placed in the recycling bin. Some cities require it to be separated from the other recyclables, but this varies based on location so it’s important to check local waste management websites for instructions. Once it’s picked up, cardboard is taken to the recycling center where the breakdown process begins. This can be separated into four steps once it is received at the facility.
How is cardboard recycled?
1. Sorting
The first step is sorting the boxes into corrugated cardboard and boxboard. Corrugated cardboard is often the type of box used for shipping retail items compared to boxboard which is the thinner cardboard used for cereal boxes, for example. This step is important as the different types of cardboard are defined as different grades and therefore may be used for different uses once broken down.
2. Shredding and pulping
The next step is shredding the cardboard and breaking the paper fibers into very small pieces. Once it’s shredded, cardboard is mixed with water and chemicals which further break down the fibers to create a slurry. The slurry is then mixed with new pulp – which is made from wood chips usually – to help firm up the mixture.
3. Filtering, contaminant removal, and de-inking
The mixture then goes through a filtering process that removes contaminants that may have been left on the boxes like string, glue, or tape. The mixture is moved to another filtering process which gets rid of any additional contaminants like plastics and metal staples. This process is similar to a centrifuge – the plastics float on top and the staples fall to the bottom to be removed. Finally, the mixture gets mixed with additional chemicals to remove any dyes or ink to prepare for the final step.
4. Finishing
The mixture is now ready to be blended with new materials and put on a flat conveyor belt to dry. A machine presses out the excess water as it dries and the formation process of the specific layers for reuse starts.
Five facts about cardboard recycling
- After recycling, cardboard remains the same quality as new cardboard – it does not lose durability or resistance.
- Recycling paper-derived products saves 80% of water compared to the production from virgin materials.
- It is estimated that one ton of recycled cardboard saves 12 to 31 trees.
- Recycling cardboard requires only 75% of the energy required to make new cardboard from virgin materials.
- Cardboard waste dumped in the landfill is about 40% of total municipal waste
Make sure you are doing your part by reducing cardboard usage, reusing existing cardboard, and recycling.

